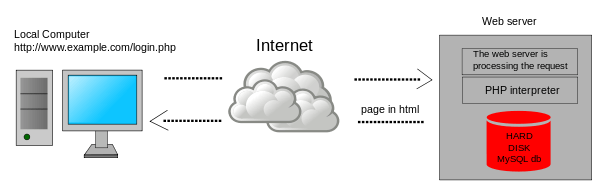
What Is PHP?
PHP code is usually processed on a web server by a PHP interpreter implemented as a module, a daemon or as a Common Gateway Interface (CGI) executable. On a web server, the result of the interpreted and executed PHP code – which may be any type of data, such as generated HTML or binary image data – would form the whole or part of an HTTP response. Various web template systems, web content management systems, and web frameworks exist which can be employed to orchestrate or facilitate the generation of that response. Additionally, this scripting language can be used for many programming tasks outside of the web context, such as standalone graphical applications and robotic drone control. This scripting language code can also be directly executed from the command line.
The standard PHP interpreter, powered by the Zend Engine, is free software released under the PHP License. This scripting language has been widely ported and can be deployed on most web servers on almost every operating system and platform, free of charge.
This scripting language evolved without a written formal specification or standard until 2014, with the original implementation acting as the de facto standard which other implementations aimed to follow. Since 2014, work has gone on to create a formal PHP specification.